In 1970, amid a national confrontation with the United States’ gun culture following the assassinations of Robert F Kennedy and Martin Luther King Jr, the historian Richard Hofstadter struggled to make sense of how the country had become the ‘only industrial nation in which the possession of rifles, shotguns, and handguns is lawfully prevalent among large numbers of its population.’ Writing for the magazine American Heritage, he expressed grave concern for a country ‘afloat with weapons – perhaps as many as 50 million of them – in civilian hands.’ If the US was afloat then, it’s flooded now.
Half a century later, Americans own approximately 400 million firearms and the country carries the unfortunate distinction of being the only one in the world in which guns are known to be the leading cause of child and adolescent death. Today, Americans live with around 1.2 guns per capita – double that of the next-highest scoring country, Yemen. Despite having less than 5 per cent of the global population, the US possesses nearly half of the world’s civilian-owned guns. Moreover, in recent years Americans have witnessed a surge in gun sales and gun-related deaths, unfolding against a backdrop of increasingly lenient gun laws across states.
In light of these developments, Hofstadter’s question takes on renewed urgency: ‘Why is it that in all other modern democratic societies those endangered ask to have such men disarmed, while in the United States alone they insist on arming themselves?’ How did the US come to be so terribly exceptional with regards to its guns?
From the viewpoint of today, it is difficult to imagine a world in which guns were less central to US life. But a gun-filled country was neither innate nor inevitable. The evidence points to a key turning point in US gun culture around the mid-20th century, shortly before the state of gun politics captured Hofstadter’s attention.
Firearm estimates derived from gun sales and surveys indicate that, in 1945, there were somewhere around 45 million guns in the US at a time when the country had 140 million people. A quarter-century later, by 1970, the number of guns doubled, whereas the population increased by a little less than 50 per cent. By 2020, the number of guns had skyrocketed to nearly tenfold of its 1945 rate, while the population grew less than 2.5 times the 1945 number.
From the mid-20th century to today, guns also changed from playing a relatively minor role in US crime to taking centre-stage. Research by the criminologist Martin Wolfgang on Philadelphia’s homicide patterns from 1948 to 1952 reveals that only 33 per cent of the city’s homicides involved a firearm. Today, 91 per cent of homicides in Philadelphia feature a gun. Similarly, the national firearm homicide rate is 81 per cent. In addition, opinion polls traced the evolution over the second half of the 20th century from Americans buying guns primarily for hunting and recreation to buying them for self-protection against other people. Together, these findings reveal a sea change in US gun culture between the mid-20th century and the present day.
US law prohibits the federal government from keeping a gun registry
So, how did this change happen? Until recently, it’s been difficult to say. The paucity of historical data on gun availability has left the origins of the country’s exceptional gun culture a mystery.
The US lacks a national gun registry, which is what most other countries use to count their gun supply. Yet, gun registration has been a hotly contested issue among US gun owners, who are concerned that state-mandated registration is a precursor to state-sponsored confiscation. Even though gun registries have been shown to reduce gun deaths, US law – specifically, the 1986 Firearm Owners’ Protection Act passed under the then president Ronald Reagan – prohibits the federal government from keeping a registry. As of today, only six US states maintain gun registries.
Without a national gun registry, researchers have had to rely on surveys and gun proxies to investigate trends related to gun availability in the US. Most of our existing data on gun prevalence comes from a few questions on the General Social Survey (GSS), which began asking US households whether they own guns in 1973 and has continued asking them every other year since. Due to its consistency over time and its nationally representative sample, the GSS is considered the gold standard of gun ownership data. It’s also been used to validate proxies for gun ownership that provide better estimates at local and state levels. Some of the most commonly used gun proxies come from hunting licences and Guns & Ammo magazine subscriptions per county, as well as the percentage of suicides with firearms per state.
Annual gun sales give us another indicator of the flow of guns into the country, but since it’s impossible to tell where those guns end up or for how long they’re in use, gun sales provide an imperfect measure of ownership over time. Moreover, gun sales data are consistently available only at the national level, and therefore do not allow researchers to exploit state- or county-level differences to explore how changes in gun ownership are related to other social factors like crime, education and public policy across the country.
It’s no wonder that when a National Research Council committee reviewed the state of research on US guns and violence in 2005, it found that ‘answers to some of the most pressing questions cannot be addressed with existing data.’ The best data available start in 1973 and are ‘limited primarily to a few questions from the General Social Survey.’ As the committee rightly pointed out:
Even the best methods cannot overcome inadequate data … Without improvements in this situation, the substantive questions in the field about the role of guns in suicide, homicide and other crimes, and accidental injury are likely to continue to be debated on the basis of conflicting empirical findings.
In other words, without the right data, even the most basic questions about guns – such as when and how the US came to have so many of them – are untestable and remain susceptible to politicised perspectives and speculative interpretations.
However, recent research conducted by Elizabeth Rasich and myself breaks new ground by expanding the data to tackle key questions of gun ownership. Researchers have long used the firearm suicide proxy, regarded as the most reliable indicator of US households with at least one gun, to explore the connection between gun ownership and various issues, including the social costs of firearms, police brutality and mass shootings. Until our newly extended dataset, this proxy was available only from 1973 onward, a time by which the country’s gun culture was already in full swing.
By extending and examining this data for household gun ownership rates – the percentage of suicides with a firearm – we sought to illuminate the enigma of the origins of the distinct gun culture in the US. The key to understanding the inception of this cultural transformation lay in accessing data on gun ownership in earlier decades. While digging in the historical records, we found that the data on firearm suicides go back to 1949, which is the first year the US vital statistics included information about suicides by gun. We hand-digitised the firearm suicide counts for each state and each year from 1949 to 1972, validated the data through a series of statistical tests and, in doing so, created what is now the longest-ranging dataset on state-level gun ownership rates to date.
With the right data in hand, we turned to our next task – making sense of the exceptionally high gun ownership rates among Americans. When trying to figure out when and how the country acquired so many guns, we initially thought the answer may lie in the civil unrest and rising crime rates of the 1960s and ’70s. Instead, we found a trajectory dating back to the mid-20th century.
Early gun culture was utilitarian, collective and state-directed
Conventional wisdom holds that the ample supply of guns has always been part of the US tradition, with consumer demand steadily meeting it. Hofstadter thought this might have to do with the ‘American historical mythology about the protective value of guns’ as ‘an important counterpoise to tyranny’. Indeed, guns helped Americans secure their independence and expand the western frontier across North America. As many know, the right of Americans to keep and bear arms is, of course, enshrined in the US constitution.
It’s true that guns have been present in the US since its inception, initially serving as tools of necessity in the colonies and on the frontier. They’ve played a key role in American imagination, culture and politics. However, in the past half-century, US gun culture has witnessed an unequivocal transformation. The historian Brian DeLay contends that the idea of a continuous gun culture in the US is a myth. His work shows that early gun culture was utilitarian, collective and state-directed; whereas in the past half-century, the emergence of new gun technologies, such as assault weapons, along with a shift towards self-defensive uses of guns, have come to define contemporary US gun culture. These developments have led gun experts like the sociologist David Yamane to identify the rise of ‘Gun Culture 2.0’ or the ‘culture of armed citizenship’ as a modern phenomenon rather than an endemic national trait.
An alternative explanation for the exceptional gun rates in the US centres on the surge of crime and civil unrest in the late 1960s to ’70s – a period coinciding with Hofstadter’s writing and a national uptick in crime. According to this perspective, the rapid rise in gun ownership rates over the past half-century is a result of escalating crime rates and eroding trust in institutions. This narrative pins the turning point of US gun culture on the spread of urban violence and the fraying of public confidence in government amid the Vietnam War, which encouraged people to put safety in their own hands, or so the story goes.
While an increase in crime and a decline in trust in the US government may have contributed to the surge in gun demand, this can’t be the full story. It’s true that the US gun stock rapidly rose during this period, however historical data from the US Department of Justice indicates that the rate of families reporting gun ownership remained stable or even declined during the 1960s and early ’70s. Moreover, our newly compiled gun ownership data going back to 1949 further challenge this explanation, pointing to an inflection point in earlier decades.
To understand the real origins of the exceptional gun culture of the US, we needed to look further back in time. Our research reveals a puzzling new trajectory: a remarkable 45 per cent increase in the household gun ownership rate from 1949 to 1990, peaking during 1990. To our surprise, more than half of this rise occurred before 1973, a period previously obscured by the lack of systematic data on gun prevalence. These new data provide a crucial historical perspective, showing that the surge in gun prevalence started before the period marked by rising crime and falling trust. In fact, our measure shows an uptick in gun prevalence beginning in the 1950s, a period defined by low homicide rates and peak trust in government, prompting questions about why and how more households acquired guns during a period of relative calm.
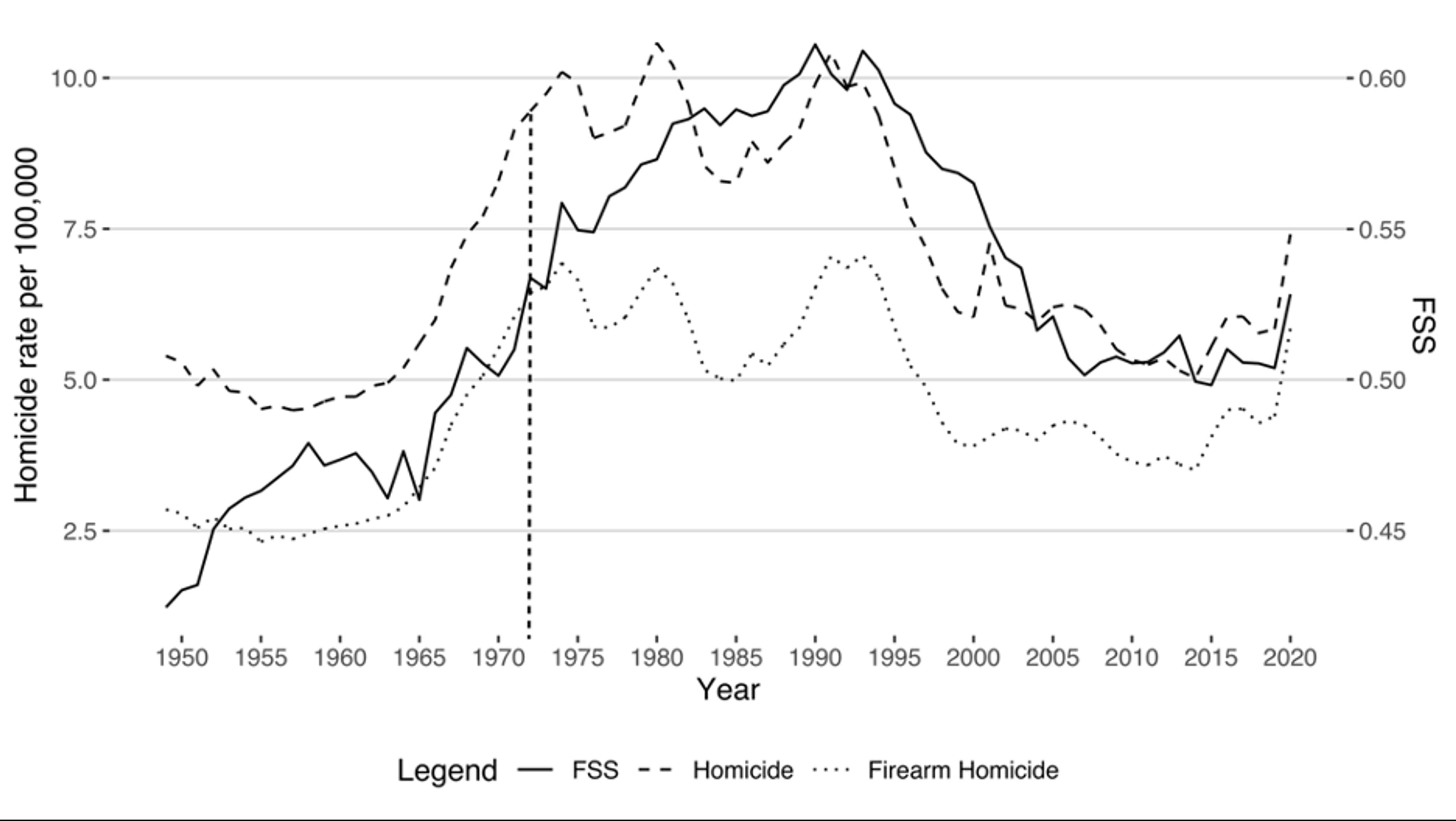
We examined the factors that were most connected to state-level increases in these rates from 1949 to 1990, the decades in which household gun ownership steadily rose and when the exceptional US gun culture took shape. We tested several different variables that could have contributed to this rise – including demographic shifts, rising crime, racial conflicts, changes in education and civil unrest, among others. We controlled for state and year differences within our sample, as is convention in scientific studies on gun ownership over time, to ensure that we weren’t comparing states with other states that have drastically different populations and gun traditions, or that the results weren’t skewed by specific years that were outliers in the data.
They mass-marketed these imported guns to consumers flush with cash
Of all the potential explanations we tested, we discovered that the post-Second World War economic boom and relaxed federal gun regulations most drove the surge in demand for guns. As unemployment rates decreased and incomes increased, firearms – once deemed a luxury or practical necessity – grew within reach for more and more Americans. Simultaneously, cultural attitudes surrounding gun ownership may have shifted, as multiple generations of Americans returning from the Second World War, the Korean War and the Vietnam War became accustomed to owning and using guns.
In his book Gun Country (2023), the historian Andrew McKevitt complements these findings with a rich tapestry of archival evidence. By weaving together gun advertisements, congressional hearings and journalistic sources, among others, McKevitt illustrates that US gun culture is unequivocally modern, specifically emerging post-1945, and from the aftermath of the Second World War and the start of Cold War politics.
Following the global demobilisation in 1945, McKevitt shows, surplus war firearms flooded the US market at dirt-cheap prices. This influx was facilitated by the ‘new gun capitalists’, a group of little-known entrepreneurs who imported and sold these guns to US consumers. They reshaped the US gun industry by establishing a mass market for civilian guns that had limited practical use elsewhere and faced stricter regulations in other countries. Capitalising on the surplus of inexpensive imported firearms, the new gun capitalists learned how to stimulate demand through marketing foreign guns as desirable consumer goods for the everyday American. They mass-marketed these imported guns to consumers flush with cash and eager to acquire these one-of-a-kind war arms from across the globe.
Magazine advertisements for mail-in orders of inexpensive guns targeted new buyers who couldn’t afford the high prices of name-brand US firearms. These ads leveraged the appeal of vintage guns as ‘authentic World War II souvenirs’ from Germany, Spain, Russia, Czechoslovakia, Japan and other war-torn countries. Post-Second World War ads can be found touting guns as among the ‘finest made by the Fascists. Carried by the crack Italian Alpine troops.’ The very gun used by Lee Harvey Oswald to assassinate the president John F Kennedy was an Italian rifle purchased from a Chicago mail-order store.

Seeking to safeguard retail prices from this new supply of foreign guns, the US gun industry pursued federal action to curb the unregulated flow of imported firearms. However, the administration of the president Dwight Eisenhower decided that redirecting global gun stockpiles into the US was preferable to them arming communist insurgents worldwide. It was the Kennedy assassination, alongside rising crime rates across US cities, that finally prompted Congress to act. The senator Thomas Dodd introduced a bill in 1963 aimed at restricting mail-order firearms. These efforts culminated in the Gun Control Act of 1968, one of the most significant pieces of gun legislation in US history.
When considering explanations for Americans’ unique gun culture, Hofstadter thought that perhaps it emerged from the enduring national idea that access to arms counters tyranny. He was partly right. As the new historical evidence shows, it was post-Second World War economic prosperity, abundant supply of cheap guns, along with increased incomes, that made way for the unique gun culture of the US. Once that gun culture took root, it flourished, helped along by public policy. Hofstadter’s theory is consistent with the fact that the steady rise in gun prevalence from 1949 to 1990 was made possible by lenient regulations, upheld by voters who saw gun rights as a symbol of freedom and the right to self-defence.
With the extended data, we can see that Hofstadter wrote at a key moment in the US history of guns. For much of US history, guns were used mainly for recreation and hunting, but during the Cold War the nation turned towards a new era of gun culture. Hofstadter died in 1970, the same year as he wrote his piece on guns. He did not live to see the transformation in the ethos around gun ownership to one of celebration that carries on to the present day.
Hofstadter believed Americans armed themselves against tyranny from above, but today’s reality is different. Guns, primarily used for hunting and sport in the mid-20th century, became largely owned for protection against fellow civilians – a reflection of a modern fear, the tyranny of uncertainty from each other.
In a country in which tens of millions of people own guns, public safety becomes a personal responsibility, and so individuals often decide that it is in their best interest to protect themselves by buying a gun. This desire to be protected against those who have guns by getting a gun, multiplied across millions of people, has resulted in an arms race that makes everyone less safe. Historical events along with policy choices have shaped this explosion in gun ownership, leading to a society in which many people have grown to associate guns with a sense of personal security. As a result, we hear all the time about guns being used in shared spaces of learning, worship and leisure.
State intervention to restrict gun availability can make a significant difference
In 1970, when thinking about how personal and political conflicts unfold in a nation with so many guns, Hofstadter asked: ‘How far must things go?’ Now, 54 years later, we can answer his question. In 2021, the US witnessed its highest number of gun deaths ever and, in 2023, its deadliest year for mass shootings. Alarming new trends include the rise of ghost guns – homemade guns made from unserialised parts, making them difficult to trace and regulate – and the increasing prevalence of military-grade automatic weapons in civilian hands. Gun ownership is only increasing, with one in five US households having purchased a gun during the COVID-19 pandemic, and new gun owners diversifying to include more women and people of colour. My friend Charles, a street outreach worker in Chicago who works with violence-involved youth, aptly summarised the situation: ‘The answer to more guns is more guns.’
This cycle of guns begetting more guns risks becoming the norm, unless there is concerted state action to reverse the trend. Research shows that state intervention to restrict gun availability can make a significant difference. By the 1990s, unprecedented crime rates prompted many US states to adopt gun restrictions that resulted in a substantial reduction in gun availability and saved tens of thousands of lives. Moreover, mass shootings in Australia, Canada and the United Kingdom motivated their governments to implement commonsense gun regulations, including bans on automatic weapons and requirements for licensing and registration. The success of these interventions offers hope that the current situation is not immutable. However, despite this progress, recent years have witnessed a reversal in both state and federal gun-control efforts. Some states have eased or repealed laws, and in 2022 the US Supreme Court limited states’ ability to restrict gun access. This has likely contributed to the recent surge in firearm deaths, particularly among Black Americans.
Examining US history helps provide insights into the present. The recent spike in gun sales and the easing of firearm restrictions across the US warrant our attention, carrying implications that transcend generations and borders. Guns acquired during the 1990s crime surge have remained in communities with consequences for current generations, and account for one-10th of the life-expectancy gap between white and Black males today. Porous state borders enable the movement of guns from lenient jurisdictions to regions with stricter laws and elevated crime rates.
Today, Americans stand at a critical juncture, facing the consequences of a nation armed against outsiders and one another alike. To tackle this issue, individuals must reject the premise that more guns equate to greater safety. Guns, lasting for more than a century, extend their impact beyond individual households, affecting the collective wellbeing of communities. The prioritisation of individual gun rights in the US over community safety has become a danger to innocents. Americans are locked in a self-perpetuating arms race that makes all of us only less safe. The exceptional gun culture of the US demands a critical reassessment of the nation’s priorities and policies to ensure a safer future – one in which it’s known for something other than guns.






