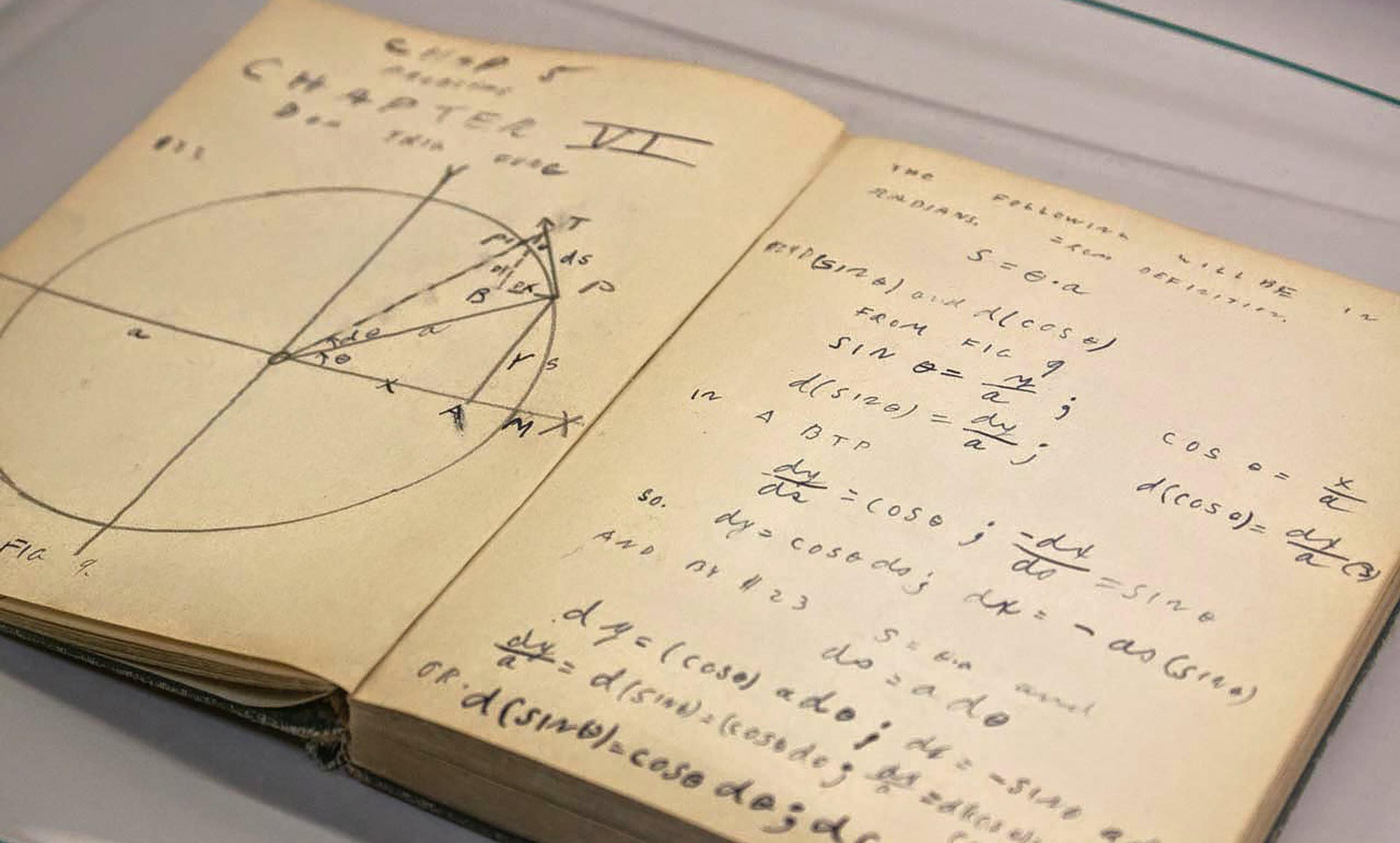Photo by Andy Rennie/Flickr
In November 2017, a gunman entered a church in Sutherland Springs in Texas, where he killed 26 people and wounded 20 others. He escaped in his car, with police and residents in hot pursuit, before losing control of the vehicle and flipping it into a ditch. When the police got to the car, he was dead. The episode is horrifying enough without its unsettling epilogue. In the course of their investigations, the FBI reportedly pressed the gunman’s finger to the fingerprint-recognition feature on his iPhone in an attempt to unlock it. Regardless of who’s affected, it’s disquieting to think of the police using a corpse to break into someone’s digital afterlife.
Most democratic constitutions shield us from unwanted intrusions into our brains and bodies. They also enshrine our entitlement to freedom of thought and mental privacy. That’s why neurochemical drugs that interfere with cognitive functioning can’t be administered against a person’s will unless there’s a clear medical justification. Similarly, according to scholarly opinion, law-enforcement officials can’t compel someone to take a lie-detector test, because that would be an invasion of privacy and a violation of the right to remain silent.
But in the present era of ubiquitous technology, philosophers are beginning to ask whether biological anatomy really captures the entirety of who we are. Given the role they play in our lives, do our devices deserve the same protections as our brains and bodies?
After all, your smartphone is much more than just a phone. It can tell a more intimate story about you than your best friend. No other piece of hardware in history, not even your brain, contains the quality or quantity of information held on your phone: it ‘knows’ whom you speak to, when you speak to them, what you said, where you have been, your purchases, photos, biometric data, even your notes to yourself – and all this dating back years.
In 2014, the United States Supreme Court used this observation to justify the decision that police must obtain a warrant before rummaging through our smartphones. These devices ‘are now such a pervasive and insistent part of daily life that the proverbial visitor from Mars might conclude they were an important feature of human anatomy’, as Chief Justice John Roberts observed in his written opinion.
The Chief Justice probably wasn’t making a metaphysical point – but the philosophers Andy Clark and David Chalmers were when they argued in ‘The Extended Mind’ (1998) that technology is actually part of us. According to traditional cognitive science, ‘thinking’ is a process of symbol manipulation or neural computation, which gets carried out by the brain. Clark and Chalmers broadly accept this computational theory of mind, but claim that tools can become seamlessly integrated into how we think. Objects such as smartphones or notepads are often just as functionally essential to our cognition as the synapses firing in our heads. They augment and extend our minds by increasing our cognitive power and freeing up internal resources.
If accepted, the extended mind thesis threatens widespread cultural assumptions about the inviolate nature of thought, which sits at the heart of most legal and social norms. As the US Supreme Court declared in 1942: ‘freedom to think is absolute of its own nature; the most tyrannical government is powerless to control the inward workings of the mind.’ This view has its origins in thinkers such as John Locke and René Descartes, who argued that the human soul is locked in a physical body, but that our thoughts exist in an immaterial world, inaccessible to other people. One’s inner life thus needs protecting only when it is externalised, such as through speech. Many researchers in cognitive science still cling to this Cartesian conception – only, now, the private realm of thought coincides with activity in the brain.
But today’s legal institutions are straining against this narrow concept of the mind. They are trying to come to grips with how technology is changing what it means to be human, and to devise new normative boundaries to cope with this reality. Justice Roberts might not have known about the idea of the extended mind, but it supports his wry observation that smartphones have become part of our body. If our minds now encompass our phones, we are essentially cyborgs: part-biology, part-technology. Given how our smartphones have taken over what were once functions of our brains – remembering dates, phone numbers, addresses – perhaps the data they contain should be treated on a par with the information we hold in our heads. So if the law aims to protect mental privacy, its boundaries would need to be pushed outwards to give our cyborg anatomy the same protections as our brains.
This line of reasoning leads to some potentially radical conclusions. Some philosophers have argued that when we die, our digital devices should be handled as remains: if your smartphone is a part of who you are, then perhaps it should be treated more like your corpse than your couch. Similarly, one might argue that trashing someone’s smartphone should be seen as a form of ‘extended’ assault, equivalent to a blow to the head, rather than just destruction of property. If your memories are erased because someone attacks you with a club, a court would have no trouble characterising the episode as a violent incident. So if someone breaks your smartphone and wipes its contents, perhaps the perpetrator should be punished as they would be if they had caused a head trauma.
The extended mind thesis also challenges the law’s role in protecting both the content and the means of thought – that is, shielding what and how we think from undue influence. Regulation bars non-consensual interference in our neurochemistry (for example, through drugs), because that meddles with the contents of our mind. But if cognition encompasses devices, then arguably they should be subject to the same prohibitions. Perhaps some of the techniques that advertisers use to hijack our attention online, to nudge our decision-making or manipulate search results, should count as intrusions on our cognitive process. Similarly, in areas where the law protects the means of thought, it might need to guarantee access to tools such as smartphones – in the same way that freedom of expression protects people’s right not only to write or speak, but also to use computers and disseminate speech over the internet.
The courts are still some way from arriving at such decisions. Besides the headline-making cases of mass shooters, there are thousands of instances each year in which police authorities try to get access to encrypted devices. Although the Fifth Amendment to the US Constitution protects individuals’ right to remain silent (and therefore not give up a passcode), judges in several states have ruled that police can forcibly use fingerprints to unlock a user’s phone. (With the new facial-recognition feature on the iPhone X, police might only need to get an unwitting user to look at her phone.) These decisions reflect the traditional concept that the rights and freedoms of an individual end at the skin.
But the concept of personal rights and freedoms that guides our legal institutions is outdated. It is built on a model of a free individual who enjoys an untouchable inner life. Now, though, our thoughts can be invaded before they have even been developed – and in a way, perhaps this is nothing new. The Nobel Prize-winning physicist Richard Feynman used to say that he thought with his notebook. Without a pen and pencil, a great deal of complex reflection and analysis would never have been possible. If the extended mind view is right, then even simple technologies such as these would merit recognition and protection as a part of the essential toolkit of the mind.