Michael Gwyther Jones/Flickr
I get apprehensive whenever someone asks me about my job. I’m a philosopher who works on the question of how language evolved, I reply. If they probe any further, I tell them that I work with the great apes at Leipzig zoo. But some people, I’ve discovered, have big problems with zoos.
Plenty of philosophers and primatologists agree with them. Even the best zoos force animals to live in confined spaces, they say, which means the animals must be bored and stressed from being watched all the time. Other critics claim that zoos are wrong even if the creatures aren’t suffering, because being held captive for human entertainment impugns their dignity. Such places ‘are for us rather than for animals’, the philosopher Dale Jamieson has written, and ‘they do little to help the animals we are driving to extinction’.
But I want to defend the value of zoos. Yes, some of them should certainly be closed. We’ve seen those terrible videos of solitary apes or tigers stalking barren cages in shopping malls in Thailand or China. However, animals have a good quality of life in many zoos, and there’s a strong moral case for why these institutions ought to exist. I’ve come to this view after working with great apes, and it might not extend to all species equally. However, since great apes are both cognitively sophisticated and human-like in their behaviour, they offer a strong test case for evaluating the morality of zoos in general.
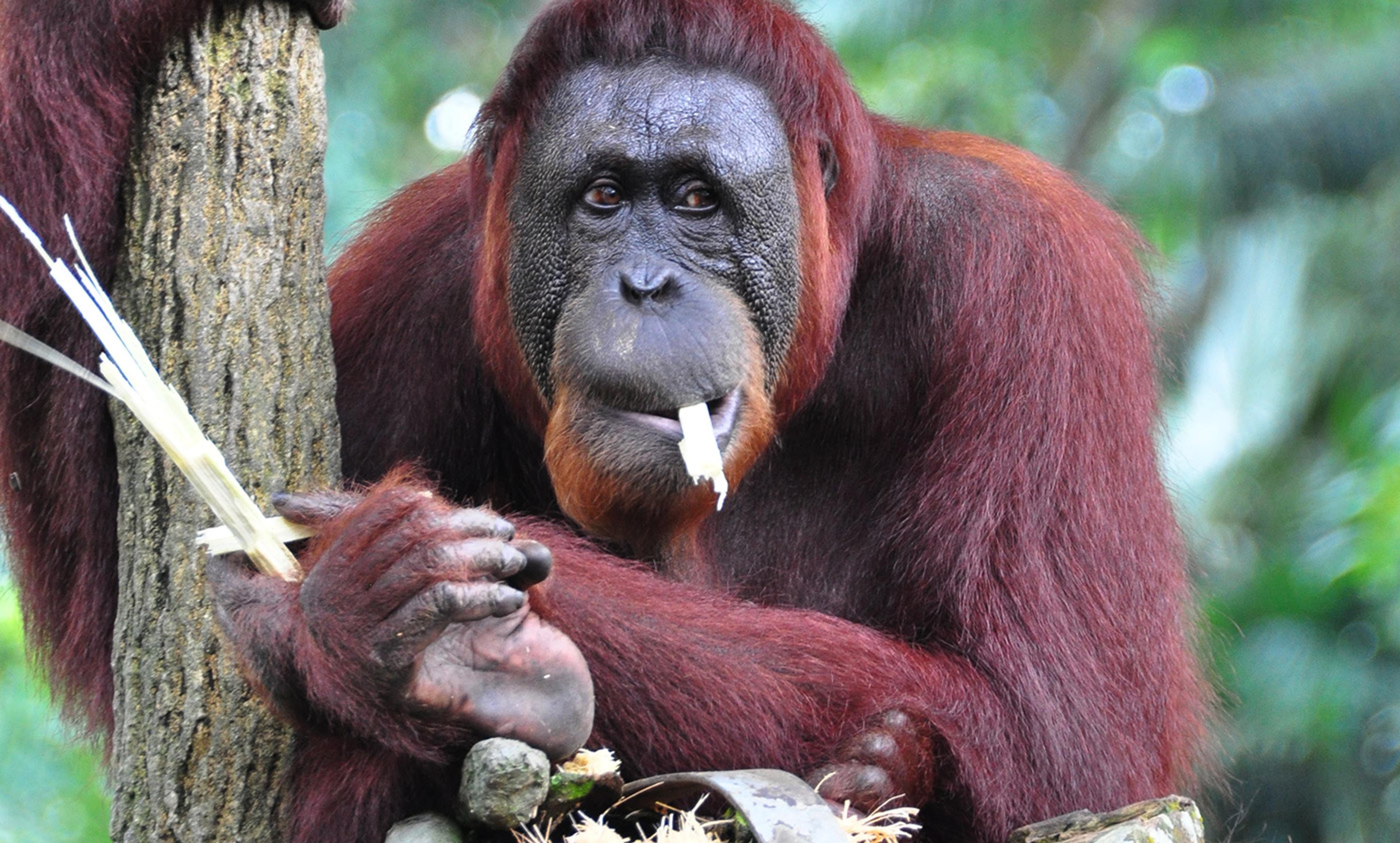
The research my colleagues and I conduct isn’t harmful to the animals and, if it goes well, it will help us get a better grasp on the cognitive differences between humans and apes. For example, we did a study with pairs of orangutans in which we tested their ability to communicate and cooperate to get rewards. We hid a banana pellet so that one orangutan could see the food but couldn’t reach it. The other orangutan could release a sliding door and push the pellet through to her partner, but wasn’t able to take it for herself. They did okay (but not great) when playing with me, and they mostly ignored each other when playing together. We then performed a similar set of studies with human two-year-olds. Compared with the apes, the two-year-olds were very good at getting the reward (stickers) when they played with an adult.
Taken together, these studies tell us something about human evolution. Unlike apes, humans are good at pooling their talents to achieve what they can’t do alone. It’s not that the apes don’t care about getting the food – they got frustrated with one another when things were going wrong, and one orangutan in particular would turn his back and sulk. However, unlike humans, they don’t seem to be able to harness this frustration to push themselves to do better.
The value of research aside, there’s an argument for zoos on the grounds of animal welfare. In the best zoos, such as Leipzig, great apes live in spacious enclosures modelled on their natural habitats, and are looked after by zookeepers who care about them deeply. Large jungle gyms keep them stimulated and stave off boredom; they’re also kept busy with ‘enrichment’ puzzles, which they can unlock with tools to get food. Zoos recognised by the two main accrediting bodies in Europe and the United States are rigorously vetted and required to take part in education and conservation programmes. And there’s no solid evidence that apes living in well-designed enclosures get stressed or disturbed by human observation.
Of course, zoos can’t provide their animals with conditions such as those in an untouched forest. But for the great apes in captivity, there’s rarely a viable alternative. There are estimated to be more than 4,000 great apes living in zoos worldwide. Most of the regions where they are found in the wild – orangutans in Indonesia, chimpanzees and gorillas in Central and West Africa, bonobos in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) – are ravaged by habitat loss, civil war, hunting and disease. As few as 880 remaining mountain gorillas survive, in two small groups in the eastern reaches of the DRC, while orangutan habitats have declined 80 per cent in the past 20 years. While some conservationists dream of rehoming zoo apes in the wild, these vanishing forests mean that it’s rarely feasible. The orangutans in Leipzig are certainly better off than they would be trying to survive in forests razed to make way for palm-oil plantations.
Since zoo apes cannot be returned to their natural environments, specialised sanctuaries are another option. But these require large plots of land that are both safe and uninhabited by existing populations, and such locations are scarce. As things stand, sanctuaries are already struggling to survive because they’re almost exclusively dependent on charitable donations. And most of them are full. In Africa and Indonesia, inhabitants are typically orphans that have been taken from the forest by hunters or palm-oil workers, who kill larger apes and kidnap the babies to sell or keep as pets. Elsewhere, sanctuaries are overflowing with retired lab apes or rescued pets. These institutions lack the capacity to accommodate the thousands of apes currently living in zoos, let alone the money that would be needed to support them.
Given the obstacles and the great expense of rehoming apes, very few places try to do so. Damian Aspinall of Howletts Wild Animal Park in England leads one of the few programmes that release gorillas back into the wild, by taking them to a protected reserve in Gabon. His intentions are heroic and hopefully the plan will succeed. Some gorillas have resettled well. But the results so far have been mixed; in 2014, five members of a family of 11 were found dead within a month of their release. We also don’t really know whether zoo-born apes possess the skills they need to survive, including the ability to retrieve different local foods, and knowledge of edible plants. Young apes learn these skills in the wild by watching the knowledgeable adults around them – but that’s an opportunity that creatures in captivity simply don’t have.
Now, all of this isn’t necessarily an ethical argument for continuing to breed apes in zoos. You might argue that if we can’t save the apes already in captivity, we should at least end breeding programmes and let the existing populations die out. However, captive breeding helps preserve the genetic diversity of endangered species. Moreover, research shows that visiting zoos makes people more likely to support conservation efforts – an effect that’s amplified by more naturalistic enclosures. So first-person encounters in zoos serve to educate visitors about the incredible lives animals lead, and to raise money for wild conservation programmes.
Allowing the ape populations in zoos to wither assumes – without justification – that their current lives are so bad as to be not worth living. It also risks inflicting harm. Boredom is a real risk for zoo animals, and it’s widely believed (although not yet scientifically established) that the presence of infants brings both interest and happiness to the families. Mixed-aged groups create collective dynamics that more closely resemble those in the wild. If we care about the welfare of captive apes, we should allow them to breed – at least in controlled ways.
One day, the prospect of returning captive apes to their natural habitats or housing them in well-funded, spacious sanctuaries might be realistic. Currently, it is not. Instead of condemning zoos, we should dedicate our efforts to supporting them: to pushing bad zoos to reform or close; to funding more research into the welfare of captive animals; and to encouraging all zoos to strive to do more for their inhabitants. That way, perhaps, I will no longer need to shy away from telling strangers what I do.