As recently as just a few decades ago, the interconnected web of experiences, thoughts and emotions known as a ‘stream of consciousness’ was widely believed to belong to humans alone. A still-accumulating body of evidence, however, strongly indicates that consciousness is far from unique to us. Rather, according to the Cambridge Declaration on Consciousness, which was signed by a group of leading scientists in 2012, it’s possessed by ‘nonhuman animals, including all mammals and birds, and many other creatures, including octopuses’.
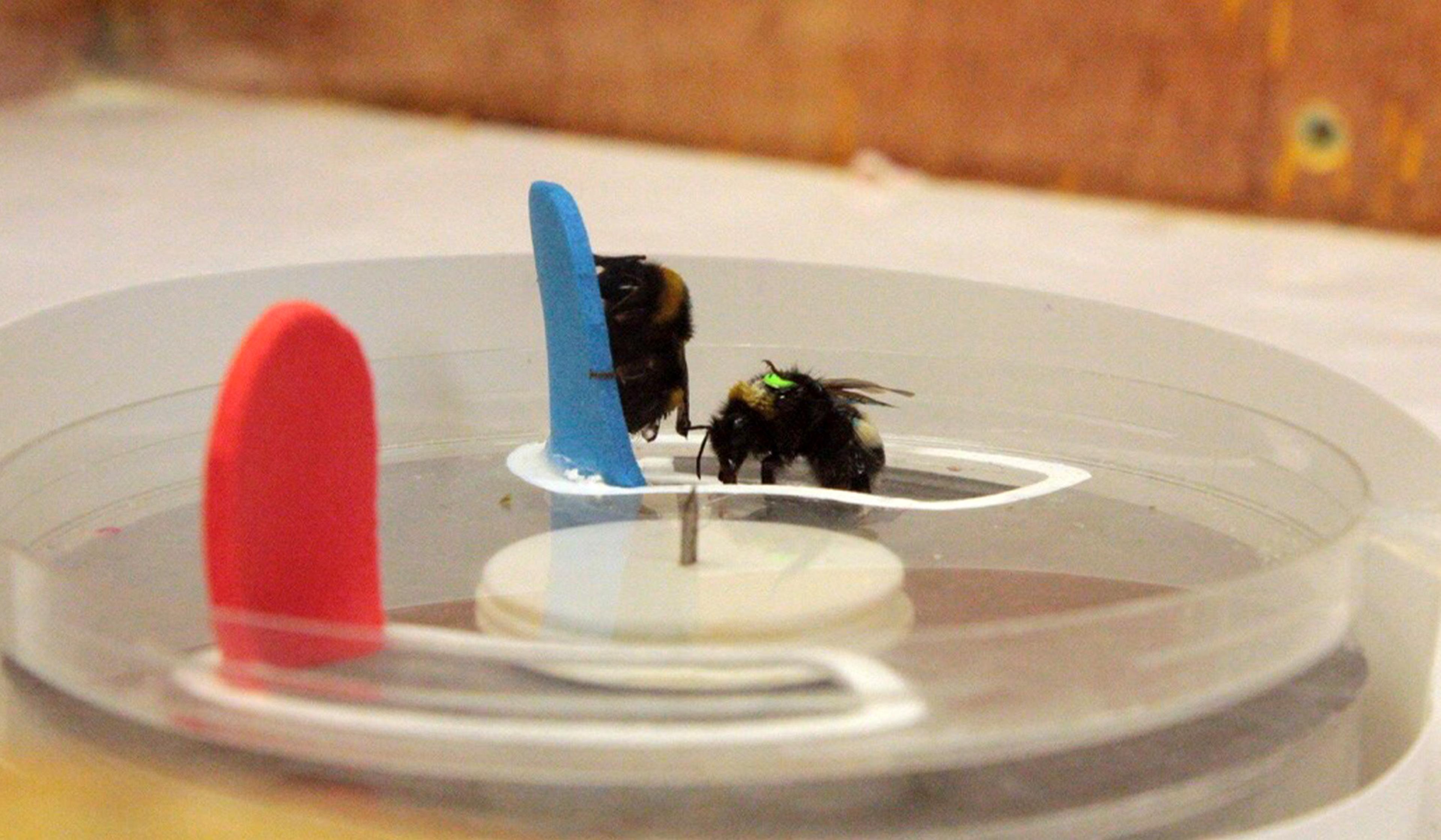
So when and why did consciousness spring from the tree of life? This brief explainer from BBC Reel outlines one groundbreaking new theory from Eva Jablonka at Tel Aviv University and Simona Ginsburg at the Open University of Israel. Centred on a concept called ‘unlimited associative learning’ – the ability to link events and outcomes, and change behaviours accordingly – their theory proposes that the advent of consciousness some 500 million years ago gave way to an evolutionary ‘arms race’ in sophisticated thinking.