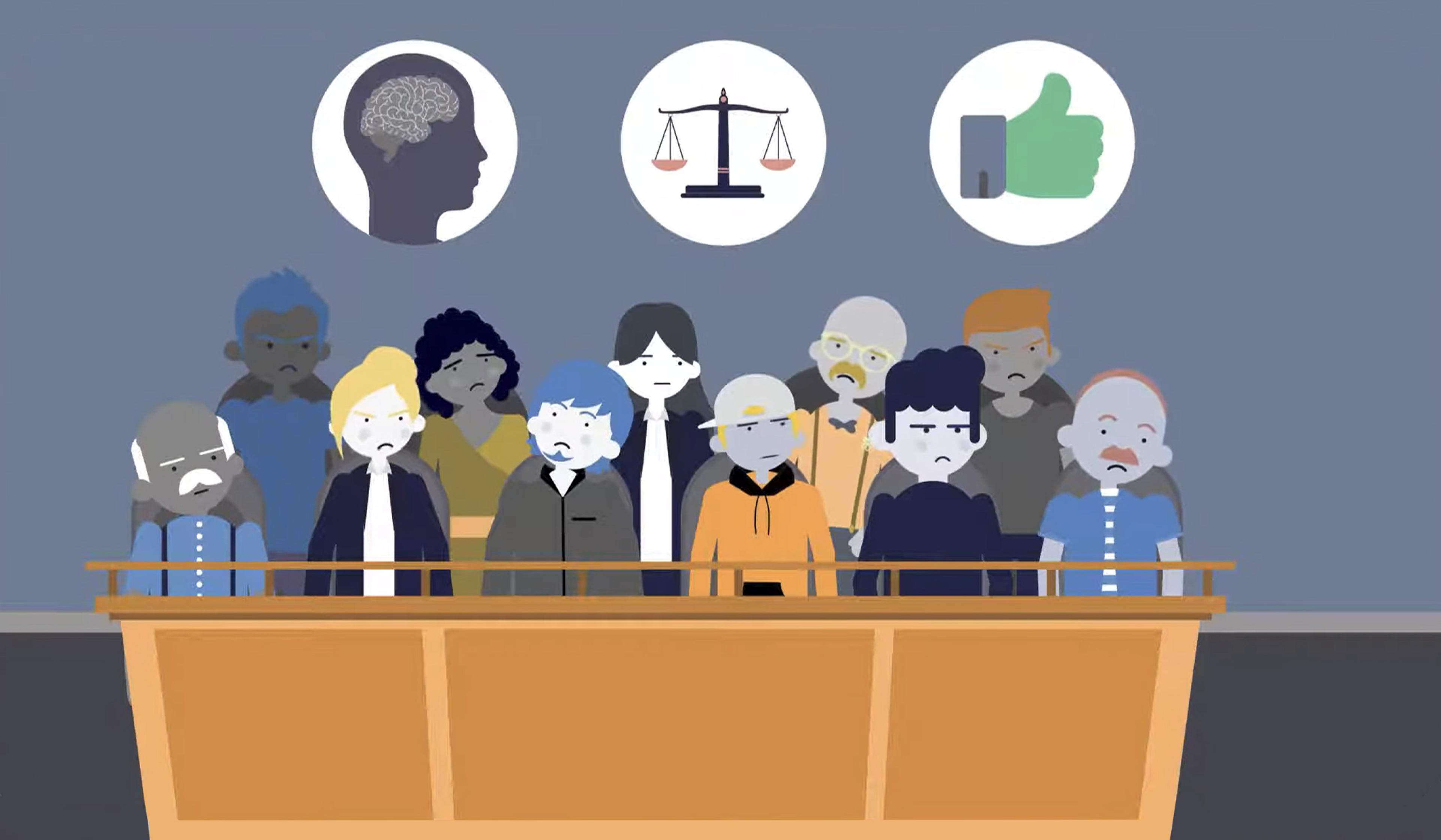
Many countries have a binary justice system that sorts defendants into two very broad categories: ‘guilty’ and ‘not guilty’. Those deemed ‘not guilty’ are often left with the stigma of a criminal record, even when the accused was overwhelmingly proven to have done nothing wrong. Meanwhile, another defendant might also be labelled ‘not guilty’, despite substantial evidence of guilt, if a single juror had some lingering doubts. And in some countries, such as the United States, the system incentivises agreements that pressure defendants to plead guilty to crimes regardless of their actual guilt. In this video from Wireless Philosophy, Barry Lam, an associate professor of philosophy at Vassar College, discusses alternatives to the prevailing two-verdict system that might more accurately reflect degrees of uncertainty – as well as some of their potential pitfalls.
Beyond ‘guilty’ or ‘not guilty’ – could a range of verdict options be more just?
Video by Wireless Philosophy
videoLogic and probability
The unresolved probability paradox that goes to the heart of scientific objectivity
8 minutes

videoPolitical philosophy
Beyond the veil – what rules would govern John Rawls’s ‘realistic Utopia’?
6 minutes

videoHuman rights and justice
Court fees and minor fines are leading to debilitating cycles of incarceration in the US
15 minutes

videoPolitical philosophy
Is the idea that democracy always benefits society misguided, or just mathematics?
7 minutes

videoThinkers and theories
The prison abolitionist who dares to envision a world without ‘unfreedoms’
16 minutes

videoEthics
If soldiers act with unjust aggression they are as culpable as civilian criminals
6 minutes

videoMetaphysics
Is the question ‘Why is there something instead of nothing?’ even worth asking?
9 minutes

videoPolitical philosophy
Want to build a just society? John Rawls said to start by ignoring your identity
2 minutes

videoKnowledge
Why David Deutsch believes good explanations are the antidote to bad philosophy
10 minutes