Symmetry is so fundamental to multicellular life that it can be easy to overlook. In fact, symmetry only seems to stand out in the notable instances where it’s quite obviously broken, such as in the case of the male fiddler crab, which possesses one smaller claw and an opposite claw that’s many times larger. In this short video, Laila Moubayidin, a Royal Society University Research Fellow at the John Innes Centre in Norwich, England, discusses why symmetry came to dominate life on Earth, and how many complex life forms, such as humans, transitioned from radial to lateral symmetry. Moubayidin also breaks down how life forms can evolve to break symmetry once they’ve established it, how some animals possess different degrees of symmetry across a lifetime, and the many ways in which humans lack perfect symmetry.
Symmetry rules life on Earth – but it comes with many fascinating exceptions
Video by the Royal Society
31 October 2022
videoBiology
For 3 billion years, life was unicellular. Why did it start to collaborate?
4 minutes

videoPhysics
If life feels out of balance, don’t worry – there’s always symmetry below the surface
4 minutes

videoMetaphysics
‘The whole thing is a monstrosity!’ How a symmetry heretic sees the Universe
8 minutes

videoPhilosophy of science
The hydra’s amazing resilience challenges ideas that all living things must die
4 minutes
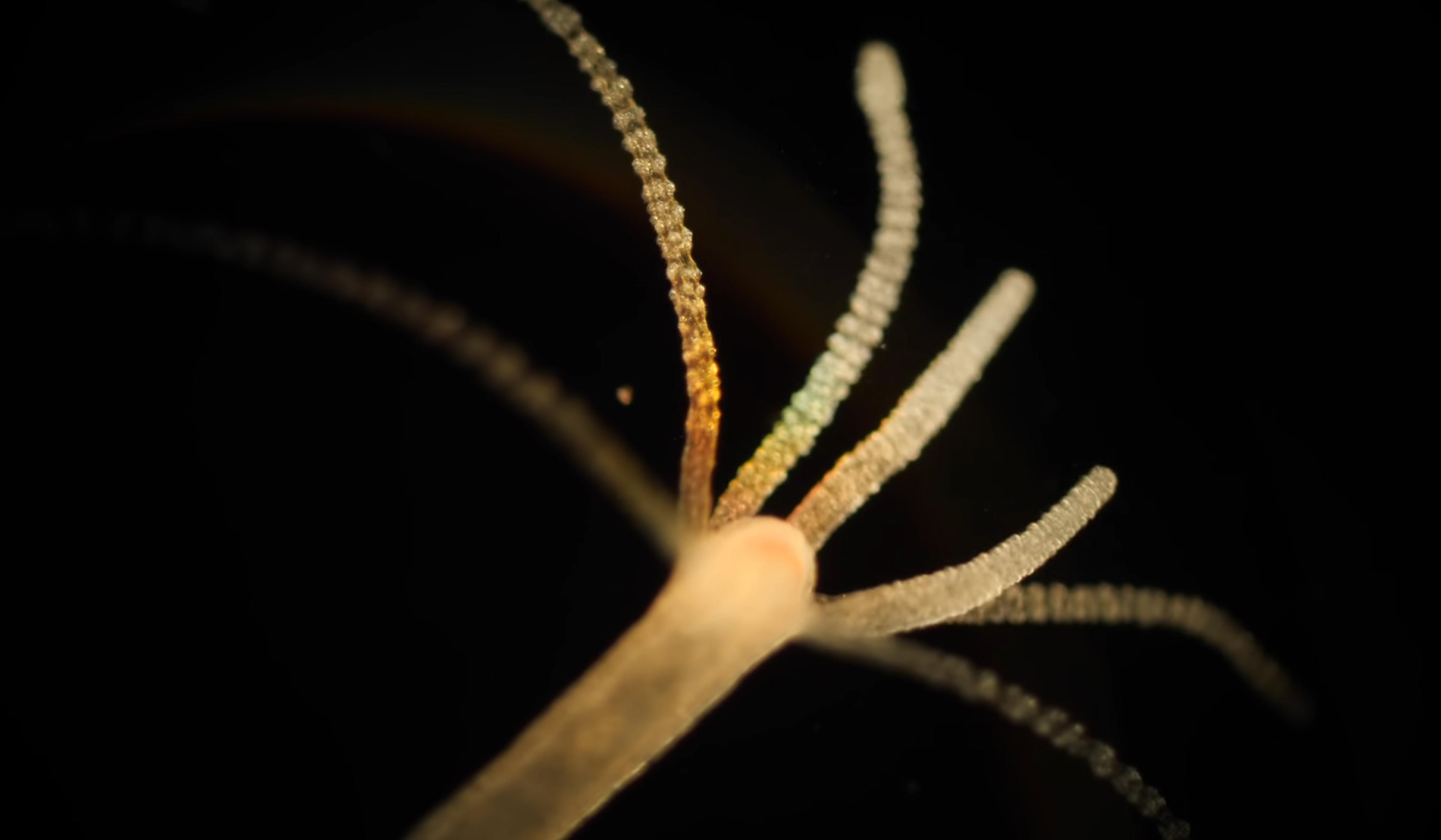

videoBiology
Blend up a hydra, and its cells will coalesce back into a full creature. How?
5 minutes

videoPhilosophy of mind
A colony of cooperating jellyfish challenges conventional ideas of individuality
2 minutes


